Simulation period
Project start time and lifetime
Income variation over time
Inflation : annual rate that will increase the amount of running costs defined in Investment and charges section during lifetime (or decrease it if the rate is negative => deflation).
Discount rate : the process of discounting is used to determine the present discounted value of a payment or revenue flow made in the future. This is how much something in the future would be worth in the present. This parameter is used in LCOE (Levelized Cost of Energy) and NPV (Net Present Value) calculations.
Production variation : annual production variation due to the degradation of the panels. Production variation can be specified as a fixed linear rate during project life or it can use the results of the aging tool. In the second case, a simulation with the aging tool must have been executed previously.
Income dependent expenses
Income tax rate : annual tax rate applied to the taxable income at the end of each year during project life.
Other income tax rate : another tax rate that could be applied to the taxable income (used in systems where multiple income taxes are applicable, such as federal and local taxes).
Dividends : rate of dividends redistributed annually to the shareholders. This rate is applied to the annual after-tax profit. For unprofitable years (negative balance), dividend amount is null.
Depreciation
Depreciation is an accounting method of allocating the cost of a tangible asset over its useful life and is used to account for declines in value. The yearly depreciation allowance is tax deductible and decreases the taxable amount.
None : depreciation is not taken into account in the financial results
Straight-line : the value of depreciable assets is reduced uniformly each year until it reaches its salvage (residual/scrap) value.
Annual depreciation allowance = (Depreciable assets - Salvage value) / Depreciation duration
Example : for a 120 000$ depreciable assets amount, with a salvage value of 20 000$ at the end of project life and an asset accounting life of 10 years, the yearly depreciation allowance would be (120 000 - 20 000) /10 = 10 000 $.
Declining balance : accelerated depreciation method that records larger depreciation expenses during the earlier years of depreciable assets life, and smaller ones in later years. This calculation method uses the straight-line depreciation rate and a depreciation coefficient :
Straight-line rate = 1 / Project life
Declining balance rate = Straight-line rate x Depreciation coefficient
Annual depreciation allowance for year t = Residual asset value for year t x Declining balance rate
When the depreciation allowance becomes lower than the straight-line depreciation allowance, the straight-line method is applied for last years of the project.
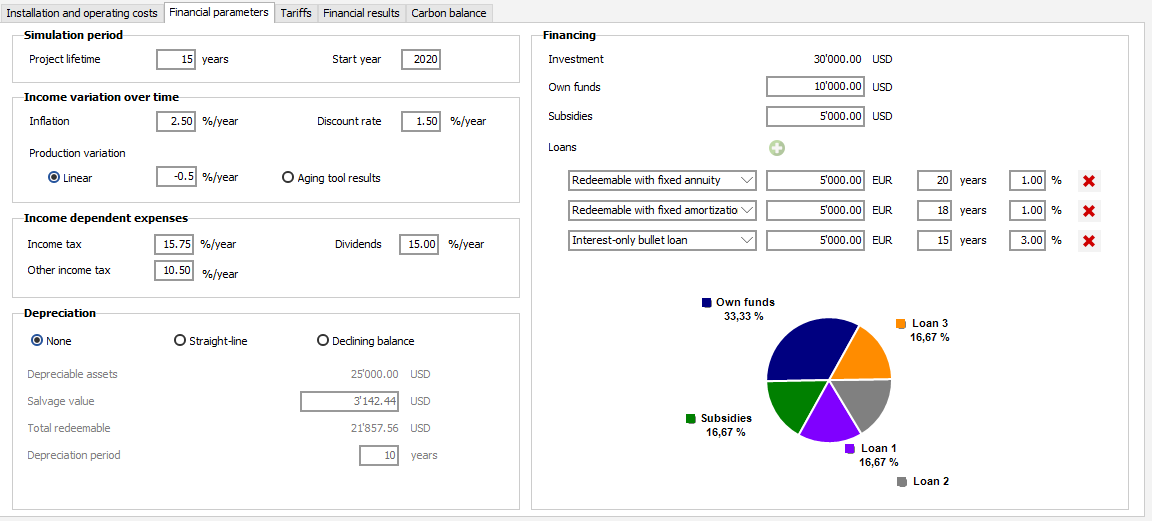
Financing
This section defines the source of funds used to finance the investment. Pvsyst allows to define three source of investment : Own funds, Subsidies and Loans. The total sum of financing funds must be equal to the total installation costs defined in Installation and operating costs dialog.
Own funds : total amount used from the capital of the company or from external investors.
Subsidies : total amount granted by the state or a public body.
Loans : amount borrowed from a bank or any lending agency. Pvsyst allows to define up to three loans with different types.
- Redeemable with fixed annuity : the reimbursed annuity is the same every year during the loan duration. The cost of interests is declining over the repayment period.
Annuity = [borrowed amount x rate] / [1 - (1 + rate) - duration in years]
- Redeemable with fixed amortization : the reimbursed amortization part is the same every year during the loan duration. Annuities are higher at he beginning of the repayment period and are falling over time
Annuity for year t = [borrowed amount / duration in years] x [1 + (duration in years - t) x rate]
- Interest-only bullet loan (also known as "in-fine" loan) : only interests are due during repayment period. Loan principal is reimbursed in full with a balloon payment at the end of loan duration.
Annuity = borrowed amount x rate
Balloon payment at the end of loan = borrowed amount